ISO/TR 6285:1980
(Main)Pipes and fittings of acrylonitrile/butadiene/ styrene terpolymer (ABS) — Chemical resistance with respect to fluids
Pipes and fittings of acrylonitrile/butadiene/ styrene terpolymer (ABS) — Chemical resistance with respect to fluids
Tubes et raccords en terpolymère acrylonitrile/ butadiène/styrène (ABS) — Résistance chimique vis-à-vis des fluides
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
TECHNICAL REPORT 6285
Published 1980-10-15
IS0 Technical Reports are subject to review within three years of
publication, with the aim of achieving the agreements necessary for
the publication of an International Standard.
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATlON*MEMYHAPOAHAR OPTAHHJAUMR no CTAHL\APTHJAUHH*ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Pipes and fittings of acrylonitrile/ butadienektyrene terpolymer (ABS) -
Chemical resistance with respect to fluids
Tubes et raccords en terpolymère acrylonitrilelbutadiènelstyrène (ABS) - Résistance chimique vis-à-vis des fluides
Technical Report 6285 was drawn up by Technical Committee ISO/TC 138, Plastics pipes, fittings and values for the transport of
fluids, and approved by the majority of its members. The reason which led to the decision to publish this document in the form of a
Technical Report rather than an International Standard is that the document represents a guide to the present technical knowledge
relating to the chemical resistance of ABS.
O Introduction
The chemical resistance values in this Technical Report are based on acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene terpolymer (ABS) chemical
resistance tables prepared within several member countries participating in the work of TC 13.
This Technical Report lists the chemicals as either suitable, unsuitable or as of limited suitability for their conveyance at the stated
temperature with ABS pipes and fittings when these are not subjected to pressure.
ABS formulations may differ not only by combining different quantities of the three principal monomers (acrylonitrile, butadiene and
styrene) but also by the means used to combine the individual monomers to produce the terpolymers, and such variations will be
somewhat reflected in the chemical resistant properties of individual formulations.
The table gives an initial classification of the chemical resistance of pipes and fittings made of ABS which is not based on any specific
formulation of ABS, but which is applicable to pipes and fittings made from ABS material covered by IS0 2580.
In general, the chemical resistance table in this document is based on industrial practice and experience gained over the last two
decades in the field of application within the chemical industry.
1 Scope and field of application
This Technical Report represents the present technical knowledge relating to the chemical resistance of ABS and will serve only as a
preliminary guide for the end user. The evaluation of chemical resistance listed in this Technical Report is based on practical ex-
perience and test results obtained through scientific investigation.
UDC 621.643.21.4 : 678.745.32-139 : 620.193.4
Ref. No. ISO/TR 6285-1980 (E)
Descriptors : piping, pipe tubes, pipe fittings, plastic tubes, acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene (ABS), chemical resistance, fluids.
0 International Organization for Standardization, 1980 0
Printed in Switzerland Price based on 7 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
ISO/TR 6285-1980 (E)
These testsl) are immersion tests at the stated temperature and normal atmospheric pressure by which the effects of the chemicals
are evaluated by changes in tensile strength, elongation at break and mass.
The results give a general indication as to the suitability of ABS pipes systems for the transport of chemical fluids, but are not a
specific guarantee in relation to any specific formulations.
The data are applicable to pipes and fittings at the listed temperatures and not subjected to applied stress due to internal pressure of
external forces such as soil loading.
2 References
IS0 527, Plastics - Determination of tensile properties.2)
I SO 2580, Plastics - Acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene (ABS) moulding and extrusion materials.
Pipes and fittings of acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene (ABS) - Designation.3)
IS0 7245,
3 Symbols and abbreviations
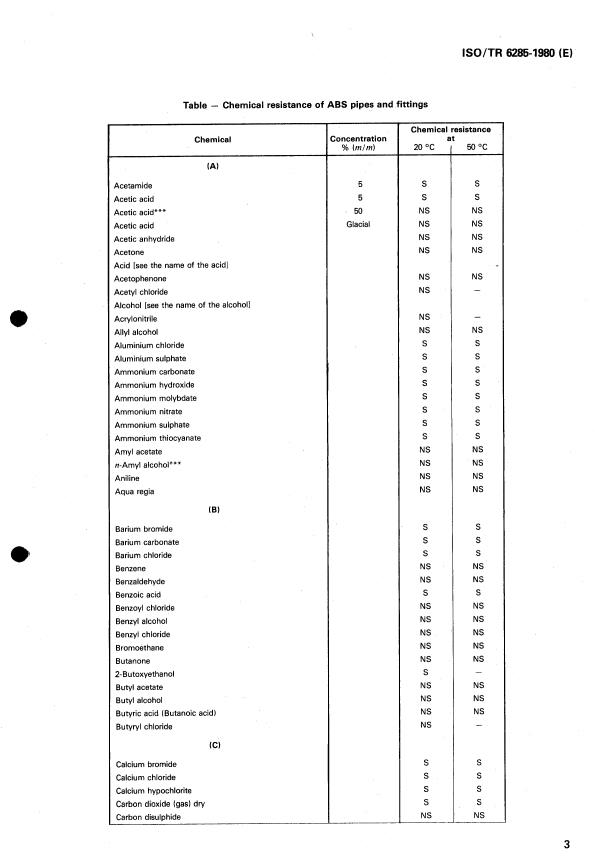
The criteria for classification, symbols and abbreviations adopted in this Technical Report are as follows :
S = Satisfactory
The chemical resistance of an ABS pipe or fitting exposed to the action of a fluid is classified as "satisfactory" when the results of
tests are acknowledged to be "satisfactory" by the majority of the countries participating in the evaluation.
L = Limited
The chemical resistance of an ABS pipe or fitting exposed to the action of a fluid is classified as "limited" when the results of tests
are acknowledged to be "limited" by the majority of the countries participating in the evaluation.
Also classified as "limited" are the resistances to the action of chemical fluids for which judgements "S" and "NS" or "S" and
"L" are pronounced to an equal extent.
In the case of certain chemicals in the mid-range of aggressive attack on ABS, the classification of "limited" has been adopted due
to the varying resistance of different specific formulations of ABS, prepared for different end users.
NS = Not Satisfactory
The chemical resistance of an ABS pipe or fitting exposed to the action of a fluid is classified as "not satisfactory" when the results
of tests are acknowledged to be "not satisfactory'' by the majority of the countries participating in the evaluation.
Also classified as "not satisfactory'' are the resistances to the action of chemical fluids for which judgements "L" and "NS" are
pronounced to an equal extent.
NOTE - Solution concentrations given in the table are expressed as a percentage by mass (unless otherwise stated). Where no concentration is
given, the chemical is tested in its natural state, or in a saturated aqueous solution (Sat. sol.), or in a solution at its normal maximum working concen-
tration iConc.1.
In the table, the resistance data (S, L, NS) are reported on the right side of each fluid, but the same data are to be considered pertaining to the ABS
pipes or fittings, not to the fluid.
1) Where testing has been carried out on a laboratory basis the criteria for evaluation have been as follows
The specimens for immersion testing in any given media at any given temperature, would be prepared by inje
...
RAPPORT TECHNIQUE 6285
Publié 1980-10-15
Les rapports techniques IS0 sont réexaminés tous les trois ans à
partir de la date de leur publication, afin de parvenir à l'accord
nécessaire pour la publication d'une Norme internationale.
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION*ME)KAYHAPOi.4HAR OPrAHHBAUHR fl0 CTAHAAPTM3AUHH.ORGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Tubes et raccords en terpolymère acrylonitrile/ butadiène/styrène (ABS) -
Résistance chimique vis-à-vis des fluides
Pipes and fittings of acrylonitrile/butadiene/styrene terpolymer (ABS) - Chemical resistance with respect to fluids.
0 Le Rapport technique 6285 a été établi par le comité technique ISO/TC 138, Tubes, raccords et robinetterie en matières plastiques '
pour le transport des fluides, et a été approuvé par la majorité de ses membres. La raison qui a conduit à publier ce document sous la
forme d'un rapport technique plutôt que d'une Norme internationale est qu'il représente un guide des connaissances actuelles concer-
nant la résistance chimique des ABS.
O Introduction
Les valeurs indiquées par le présent Rapport technique ont pour base les tableaux de résistance chimique des terpolymères
acrylonitrile/butadiène/styrène (ABS), établis dans plusieurs pays membres de I'ISO/TC 138.
Ce Rapport technique donne une liste des produits chimiques qui peuvent ou non être véhiculés (ou qui peuvent l'être seulement dans
des conditions bien définies), par les tubes et les raccords en ABS à des températures données, mais sans pression.
Les ABS peuvent différer entre eux, car en faisant varier, non seulement les proportions respectives des trois comonomères (acryloni-
trile, butadiène et styrène), mais aussi le mode de préparation, il peut se produire une variation de la résistance chimique.
*
La classification indiquée est préliminaire. Elle ne correspond pas à une formule particulière d'ABS et s'applique aux tubes et aux rac-
cords en ABS conformes à I'ISO 2580.
Les tableaux de résistance de ce document sont, en général, basés sur la pratique industrielle et sur l'expérience acquise au cours des
deux dernières décades dans l'industrie chimique.
1 Objet et domaine d'application
Le présent Rapport technique représente l'état des connaissances techniques actuelles concernant la résistance chimique des ABS et
peut servir seulement de guide préliminaire aux utilisateurs. Les résistances chimiques indiquées ont ici pour base l'expérience prati-
que, ainsi que des résultats d'essais de laboratoire.
CDU 621.643.21.4 : 678.745.32-139 : 620.193.4 Réf. no : ISO/TR 6285-1980 (FI
Descripteurs : tuyau, tuyauterie, raccord de tuyauterie, tube en matière plastique, acrylonitrile/butadiène/styrène (ABS), résistance chimique,
@
fluide.
8
ce O Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1980 O
t
imprimé en Suisse
Prix basé sur 7 pages
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
ISO/TR 6285-1980 F
II s’agit alors d’essais’) d’immersion à la pression atmosphérique et à des températures données, avec lesquels les effets des fluides
sont évalués avec la détermination des changements des caractéristiques comme la résistance en traction, l’allongement à la rupture
et la masse.
Les résultats donnent une indication générale relative à la possibilité d‘utiliser des canalisations en ABS pour le transport des fluides
chimiques; mais ils ne constituent pas une garantie pour une formule particulière d’ABS.
Les résultats sont applicables aux tubes et raccords, aux températures mentionnées dans le texte, non soumis à une pression interne,
ni à des contraintes mécaniques externes telles que celles dues à la poussée des terres.
2 Références
IS0 527, Matières plastiques - Détermination des caractéristiques en traction.2)
Plastiques - Matières à mouler et à extruder en acrylonitrile/butadiène/styrène (ABSJ.
IS0 2580,
IS0 7245, Tubes et raccords en acrylonitrile/butadiène/styrène (ASA) - Désignation.3)
3 Symboles et abréviations
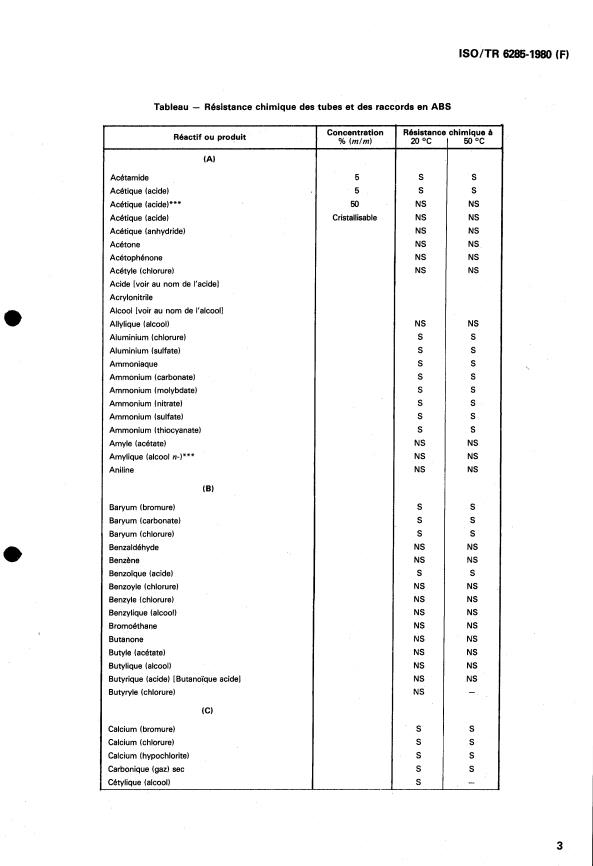
Les critères de classification, les symboles et les abréviations adoptés dans le présent document sont les suivants :
S = Satisfaisant
La résistance chimique d’un tube ou d’un raccord en ABS soumis à l’action d‘un fluide est classé ((satisfaisante)) lorsque les résul-
tats des essais sont reconnus comme étant ((satisfaisants)) par la majorité des pays participant à l‘estimation.
L = Limité
La résistance chimique d’un tube ou d’un raccord en ABS soumis à l’action d’un fluide est classée dimitée)) lorsque les résultats
des essais sont reconnus comme étant «limités» par la majorité des pays participant à l’estimation.
Sont également classées «limitées» les résistances à l’action des fluides pour lesquels un nombre égal d’appréciations «S» et «NS»
ou «S» et «L» sont prononcées.
Dans le cas de certains réactifs chimiques, intermédiaires en ce qui concerne leur aggressivité contre I’ABS, la classification
«limité» a été adoptée du fait que leur action n’est pas la même sur les différent types d’ABS, mis au point pour les divers utilisa-
teurs.
NS = Non satisfaisant
e
La résistance chimique d’un tube ou d’un raccord en ABS soumis à l’action d’un fluide est classée «non satisfaisante)) lorsque les
résultats des essais sont reconnus comme étant «non satisfaisants)) par la majorité des pays participant à l‘estimation.
Sont également classées «non satisfaisantes)) les résistances à l’action des fluides pour lesquels un nombre égal d’appréciations
c(L» et «NS» sont prononcées.
NOTE - Les concentrations données dans le tableau sont exprimées en pourcentage en masse (sauf indication particulière différentes). En général,
lorsqu’il n‘est pas fait mention de la concentration, le fluide chimique a été examiné soit dans son état naturel, soit en solution aqueuse saturée (Sol.
sat.), soit à sa concentration normale maximale de travail (Conc.).
Dans le tableau, les données de résistance (S, L, NS) sont indiquées en regard de chaque fluide, mais doivent être considérées comme se rapportant
aux tubes et raccords en ABS, et non aux fluides.
1) Lorsque les essais sont réalisés dans un laboratoire, la méthode utilisée est la suivante :
Les éprouvettes, destinées aux essais d’immersion dans un fluide à une température donnée, sont moulées par injection ou découpées à I‘emporte-
pièce dans les tubes, aux dimensions du type B de I’ISO 527 (anciennement type 1 de I‘ISO/R 527)
...


Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.